The Hidden World of Ants: Exploring the Intricate Societies of Insects
Journey into the secret lives of ants and discover the fascinating world of insect societies. Explore the complexities of ant colonies, their communication methods, and the roles each ant plays in maintaining their intricate social structure.
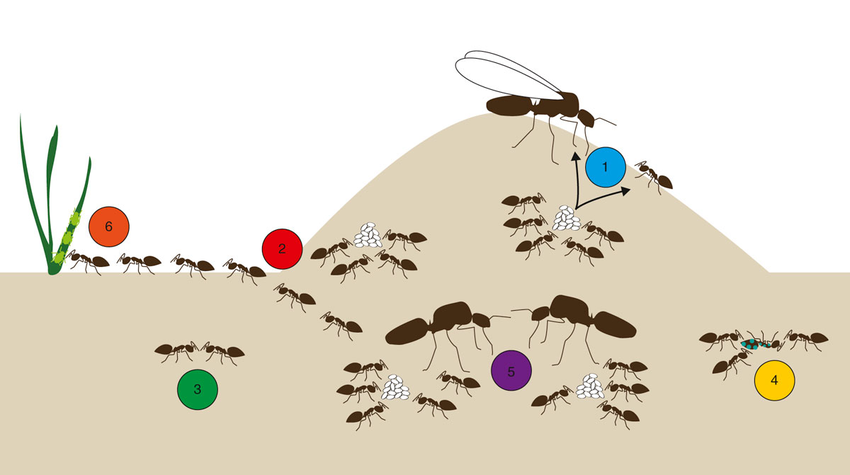
Introduction

Ants, despite their small size, exhibit remarkable social behaviors and organizational structures. In this article, we delve into the mysterious lives of ants, uncovering the intricacies of their societies and the fascinating dynamics that govern their behavior.
The Diversity of Ant Species
Ants are among the most diverse and abundant insects on Earth, with over 12,000 known species inhabiting various ecosystems worldwide. From tiny garden ants to colossal leaf-cutter ants, each species has evolved unique adaptations to suit its environment and lifestyle.
Anatomy of an Ant Colony
At the heart of every ant society lies the colony, a complex network of individuals working together for the collective good. Within the colony, ants are divided into castes, each with specific roles and responsibilities that contribute to the colony's survival and success.
Communication Among Ants
Ants communicate primarily through chemical signals known as pheromones, which convey information about food sources, nest locations, and potential threats. By detecting and responding to these chemical cues, ants can coordinate their activities and maintain social cohesion within the colony.
Division of Labor
One of the key features of ant societies is the division of labor, where different individuals specialize in specific tasks such as foraging, caring for young, or defending the colony. This division of labor maximizes efficiency and ensures that all essential roles are fulfilled.
Queen and Reproduction
At the heart of every ant colony is the queen, whose primary role is to reproduce and maintain the population. Queens produce vast numbers of eggs, which develop into workers, drones, and new queens, perpetuating the colony's existence through successive generations.
Ant Architecture
Ants are skilled builders, capable of constructing elaborate nests and tunnels using a combination of soil, saliva, and other materials. These structures serve as shelter, nurseries for young ants, and storage chambers for food, reflecting the ingenuity and adaptability of ant societies.
Interactions with Other Species
Ants interact with a wide range of other organisms, forming symbiotic relationships with some species while engaging in competitive or predatory behavior with others. These interactions shape ecosystems and influence the distribution and abundance of both ants and their ecological partners.
The Role of Ants in Ecosystems
Ants play crucial roles in ecosystems as predators, scavengers, seed dispersers, and soil engineers. Their activities influence nutrient cycling, plant growth, and pest regulation, making them essential contributors to ecosystem health and stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the secret lives of ants offer a window into the fascinating world of insect societies and the complex behaviors that govern their interactions. By studying ants, we gain valuable insights into social organization, communication, and cooperation, shedding light on the fundamental principles that shape life on Earth.
FAQs
- How many ant species are there?
- There are over 12,000 known species of ants, inhabiting diverse ecosystems worldwide.
- How do ants communicate?
- Ants communicate primarily through chemical signals known as pheromones, which convey information about food sources, nest locations, and potential threats.
- What is the role of the queen in an ant colony?
- The queen's primary role is to reproduce and maintain the population of the colony by laying eggs.
- What are some examples of ant interactions with other species?
- Ants form symbiotic relationships with some species, such as aphids and fungi, while engaging in competitive or predatory behavior with others, such as termites and rival ant colonies.
- What ecological roles do ants play?
- Ants play crucial roles in ecosystems as predators, scavengers, seed dispersers, and soil engineers, influencing nutrient cycling, plant growth, and pest regulation.