Best Data Security Tools and Practices
This blog explores the best tools and practices for safeguarding your data from unauthorized access and breaches.
In our data-driven world, protecting sensitive information is more important than ever. This blog explores the best tools and practices for safeguarding your data from unauthorized access and breaches.
1. Understanding Data Encryption

Data encryption is essential for protecting your data. It involves converting information into a coded format that only authorized individuals can read with the correct decryption key. Even if data is intercepted, encryption ensures it remains unreadable without proper authorization. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is widely used for its strong security and efficiency.
To protect your data effectively, use end-to-end encryption for information in transit, like emails and online transactions, and data at rest, such as files on servers or laptops. Regularly updating encryption keys and algorithms is vital to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities. Implementing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enhances secure digital communication and authentication, further strengthening your data protection strategy. Simply put, data encryption is a non-negotiable part of modern data security, providing a robust defense against unauthorized access.
2. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
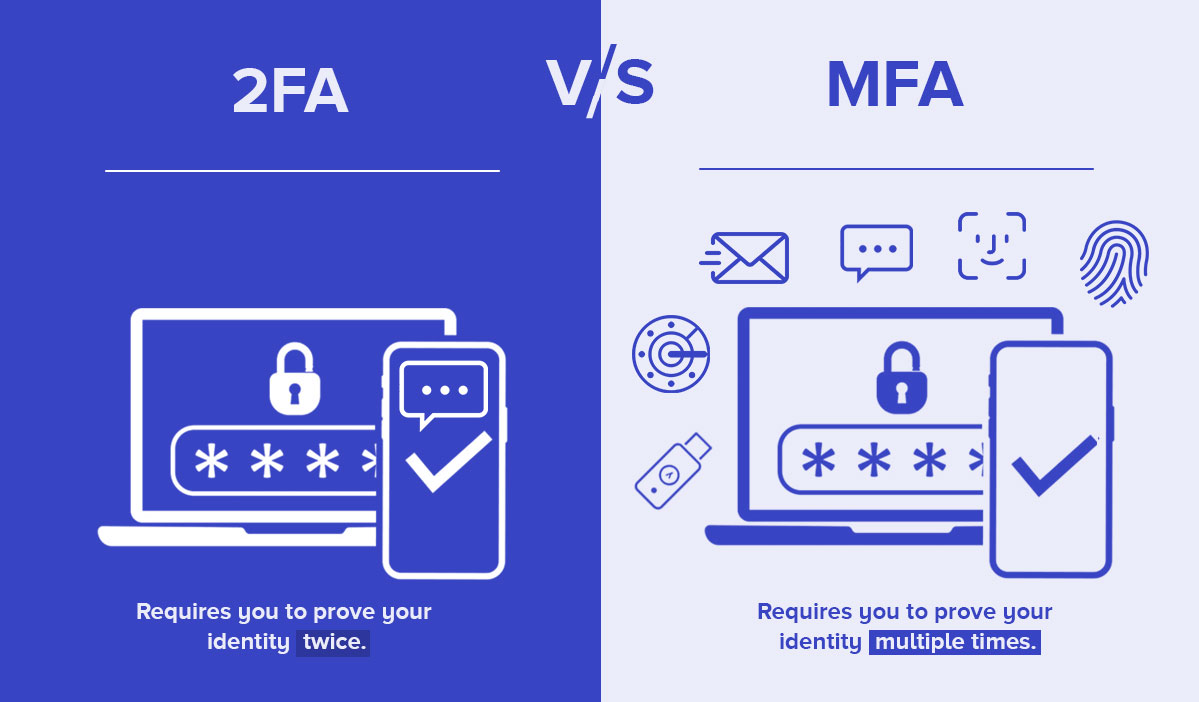
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is crucial for enhancing data security. It requires users to provide two or more verification methods to access resources. These methods can include something you know (like a password), something you have (like a security token or smartphone), and something you are (such as a fingerprint or facial recognition).
MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one method is compromised. Tools like Google Authenticator, Authy, and hardware tokens like YubiKey offer various options for implementing MFA. It’s important to choose MFA tools that integrate smoothly with your current IT setup without disrupting user experience. Applying MFA across all critical systems, including email, cloud services, and corporate networks, ensures comprehensive security. As cyber threats evolve, MFA’s layered security approach remains essential for ongoing data protection.
3. Leveraging Advanced Threat Detection Systems

Advanced threat detection systems are key to identifying and neutralizing cyber threats in real-time. These systems use machine learning, behavioral analytics, and artificial intelligence to detect unusual activities that traditional security measures might miss. Tools like Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions are critical components.
IDS monitor network traffic for suspicious behavior and provide alerts and reports, while EDR focuses on endpoints to detect, investigate, and respond to threats. Anomaly detection, a crucial feature of advanced threat detection, compares current user behavior to historical data to spot irregular activities that may signal a security breach. Implementing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems further enhances security by collecting and analyzing data from various tools. Regular updates and tuning of these systems are necessary to adapt to changing threats, ensuring continuous and proactive data protection.
4. Performing Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are fundamental for maintaining a strong data protection framework. These evaluations help identify weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and non-compliance with security policies. A thorough audit includes reviewing network security, application security, data storage practices, and user access controls.
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, is also essential. Security experts simulate attacks to uncover potential vulnerabilities. Using frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, and GDPR guidelines ensures compliance with industry standards and legal requirements. It’s crucial to prioritize audit findings to address the most critical vulnerabilities first, reducing immediate risks. Regular employee training and awareness programs are also vital, as human error often leads to security breaches. By promoting a culture of security mindfulness, organizations can reduce the risk of data leaks from within. In short, consistent security audits and assessments help identify, address, and mitigate risks, enhancing overall data protection.
5. Utilizing Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions
Backup and disaster recovery solutions are critical for maintaining data integrity and availability in the event of accidental deletions, hardware failures, or cyber-attacks. A robust backup strategy includes regular, automated backups of important data, stored in multiple locations—both on-site and off-site—to mitigate various risks.
Cloud-based backup services like AWS Backup, Microsoft Azure Backup, and Google Cloud Backup offer flexible and scalable solutions tailored to your needs. A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is also crucial, outlining procedures for restoring data and resuming business operations after an incident. DRPs should be regularly tested with full-scale mock drills to ensure readiness in an actual crisis. Continually monitoring and updating backup systems to include new data and applications, as well as encrypting backup data, add extra layers of security. In conclusion, effective backup and disaster recovery strategies protect your data and ensure continuity and resilience against unexpected disruptions.